The quest for harnessing solar energy dates back centuries, but significant technological advancements over the past few decades have revolutionized how we capture and utilize the sun’s power. This evolution encompasses two primary technologies: photovoltaics (PV) and solar thermal systems. Each has its unique principles, applications, and benefits. This comprehensive guide delves into the journey from the early days of solar photovoltaics to the innovative world of solar thermal energy.
The Dawn of Photovoltaics
The Birth of Photovoltaic Technology
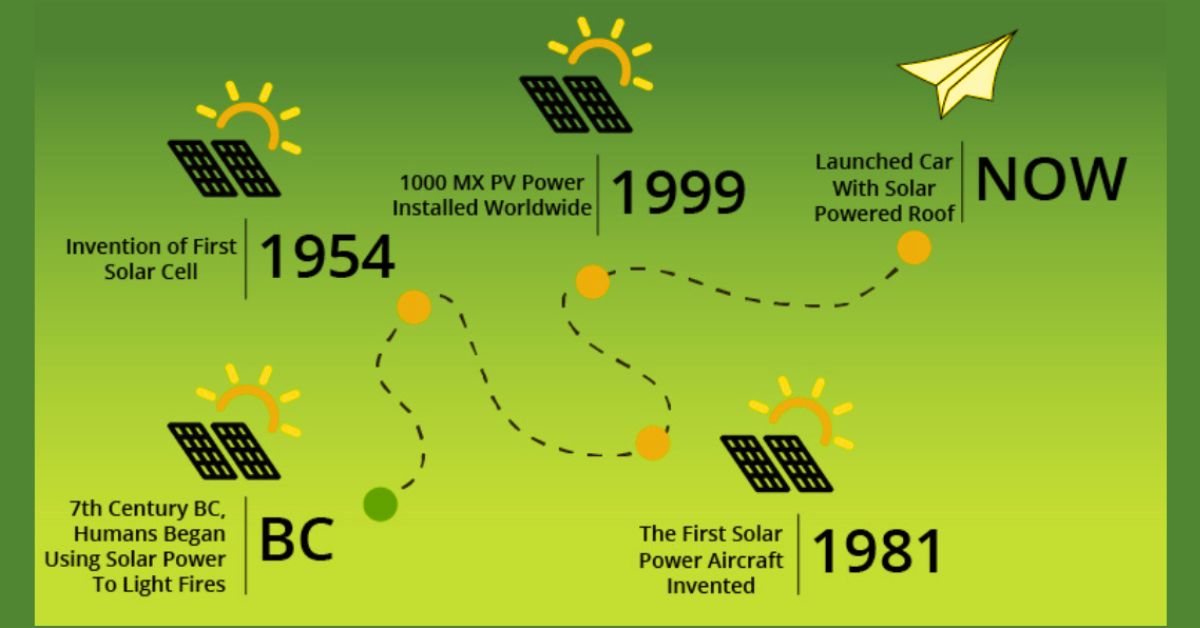
The photovoltaic effect, the phenomenon where light is converted into electricity, was first observed by French physicist Edmond Becquerel in 1839. However, it wasn’t until the mid-20th century that practical PV cells were developed. In 1954, Bell Laboratories created the first practical silicon solar cell, marking the birth of modern photovoltaics.
Early Applications and Development
Initially, PV cells were primarily used in space applications, powering satellites and space probes. The high cost of production limited their use in terrestrial applications. However, ongoing research and development led to improved efficiencies and reduced costs, gradually making solar panels viable for broader use.
The Solar Boom
The 1970s oil crisis spurred interest in alternative energy sources, leading to increased investment in solar technology. Governments worldwide began to offer incentives and subsidies, encouraging the adoption of solar power. By the early 21st century, PV technology had made significant strides, becoming a viable option for residential, commercial, and industrial energy needs.
The Rise of Solar Thermal Systems
Understanding Solar Thermal Energy
While photovoltaics convert sunlight directly into electricity, solar thermal systems harness solar energy to generate heat. This heat can be used for various applications, such as heating water, space heating, and generating electricity through steam turbines. Solar thermal technology can be broadly categorized into three types:
- Low-Temperature Systems: Used for residential heating and hot water.
- Medium-Temperature Systems: Employed in commercial and industrial settings.
- High-Temperature Systems: Utilized in concentrated solar power (CSP) plants for electricity generation.
Key Developments in Solar Thermal Technology
Early Innovations
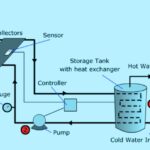
The concept of solar thermal energy dates back to the 18th century when Swiss scientist Horace-Benedict de Saussure created a solar collector. However, practical solar thermal systems began to emerge in the 20th century. The first commercial solar water heater was patented in 1891 by Clarence Kemp in the United States, laying the foundation for modern solar thermal technology.
Advancements in Concentrated Solar Power (CSP)
The late 20th and early 21st centuries saw significant advancements in CSP technology. CSP systems use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a small area, generating high temperatures. This heat is then used to produce steam, driving turbines to generate electricity. Innovations in CSP include parabolic troughs, solar power towers, and dish Stirling systems, each offering unique methods for concentrating and utilizing solar energy.
Photovoltaics vs. Solar Thermal: A Comparative Analysis
Efficiency and Applications
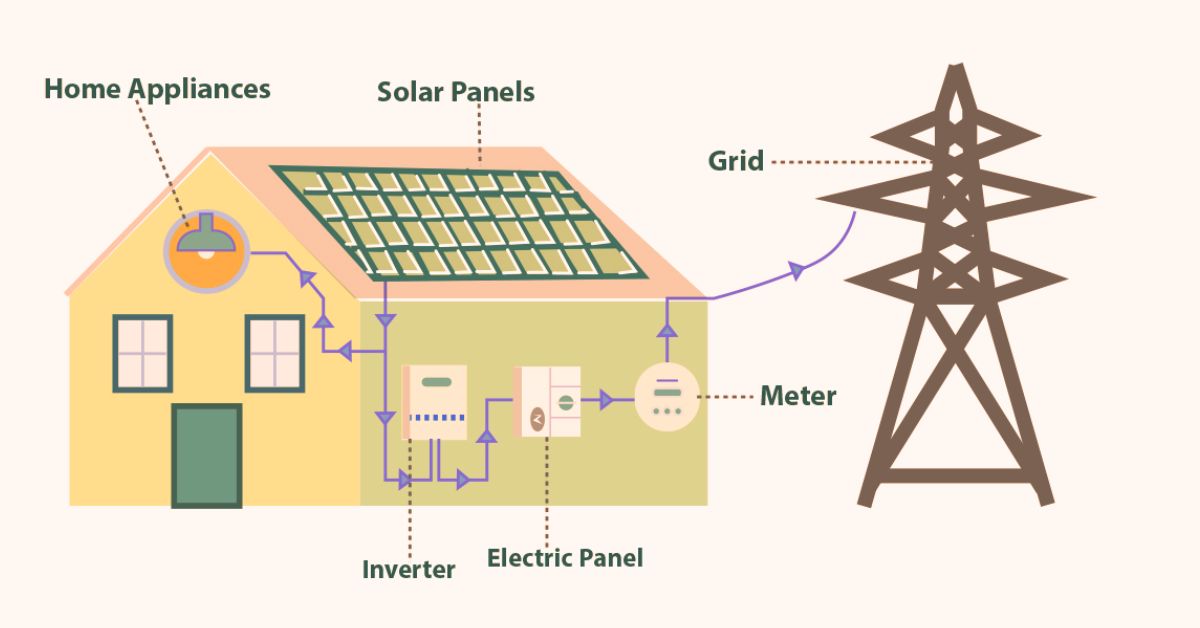
- Photovoltaics: PV systems are highly efficient at converting sunlight into electricity, making them ideal for applications where direct electrical power is needed. They are commonly used in residential rooftop installations, solar farms, and portable solar devices.
- Solar Thermal: Solar thermal systems are more efficient at capturing and storing heat. They are best suited for applications requiring thermal energy, such as water heating, space heating, and industrial processes. CSP systems are particularly effective for large-scale power generation.
Cost and Installation
- Photovoltaics: The cost of PV systems has decreased significantly over the years, making them accessible to a wider audience. Installation is relatively straightforward, involving the placement of solar panels on rooftops or ground-mounted arrays.
- Solar Thermal: While solar thermal systems can be more complex to install due to the need for collectors, heat exchangers, and storage tanks, they offer long-term savings and efficiency for specific applications. CSP systems, in particular, require significant initial investment but provide substantial energy output.
Environmental Impact
Both PV and solar thermal systems offer substantial environmental benefits by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. However, solar thermal systems, particularly CSP, can provide a more consistent and reliable energy supply, as they can store heat for use during periods without sunlight.
The Future of Solar Power
Integrating PV and Solar Thermal Technologies
The future of solar power lies in the integration of PV and solar thermal technologies, maximizing the benefits of both. Hybrid systems that combine PV panels with solar thermal collectors are being developed to provide comprehensive energy solutions, catering to both electrical and thermal energy needs.
Technological Innovations
Ongoing research is focused on improving the efficiency and affordability of solar technologies. Innovations such as perovskite solar cells, advanced heat storage materials, and smart grid integration are poised to revolutionize the solar industry, making solar power more accessible and efficient.
Global Adoption and Policy Support
As governments worldwide continue to recognize the importance of renewable energy, supportive policies and incentives are expected to drive the adoption of solar technologies. The commitment to reducing carbon emissions and achieving sustainability goals will further propel the growth of both PV and solar thermal systems.
Conclusion
The evolution of solar power from early photovoltaic cells to advanced solar thermal systems showcases the remarkable progress in harnessing the sun’s energy. Both technologies play crucial roles in the transition to a sustainable energy future, offering complementary solutions for diverse energy needs. As technological advancements continue and global support grows, solar power will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of renewable energy innovations, paving the way for a cleaner, greener planet.